Motor Duty Cycle
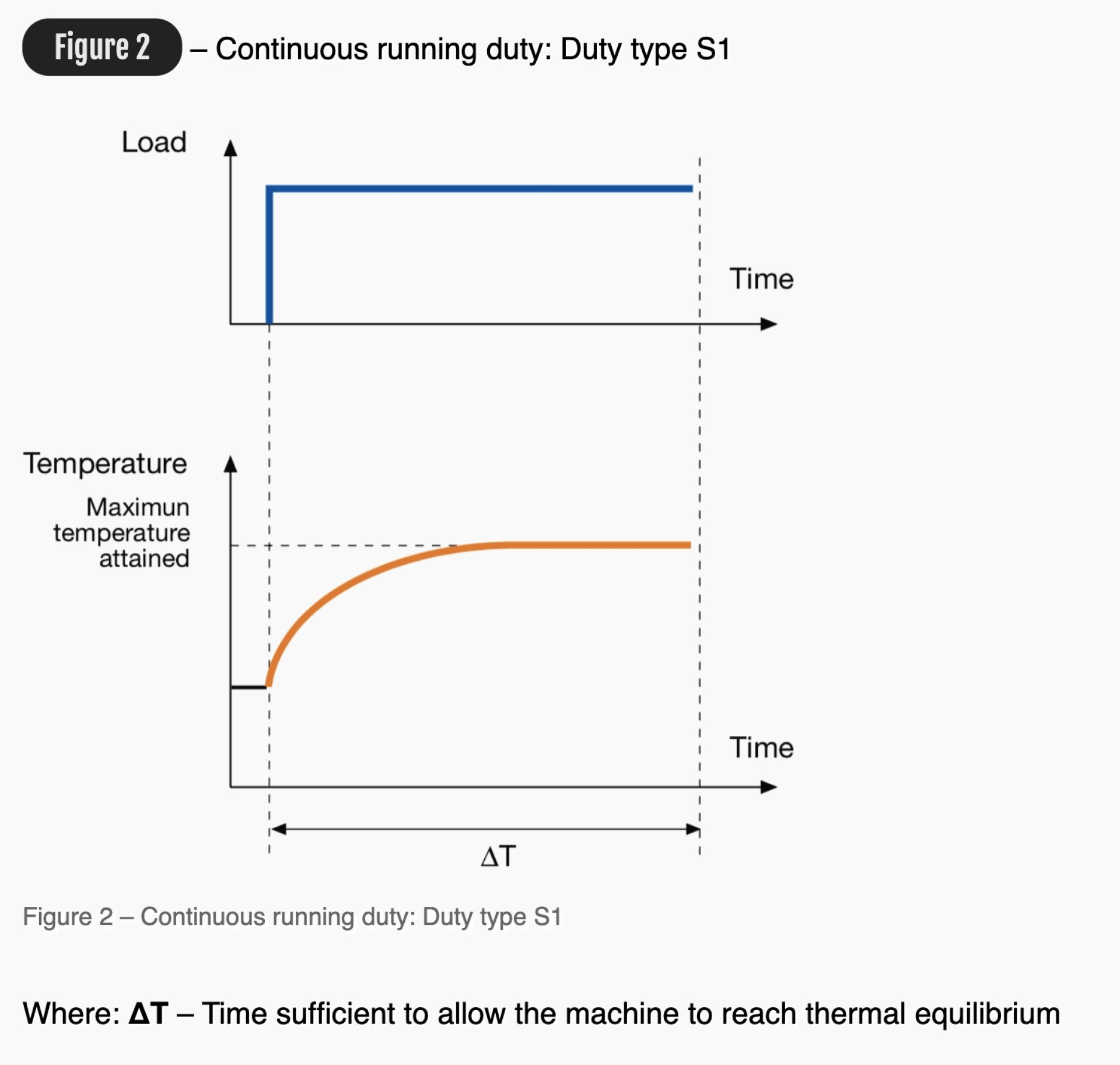
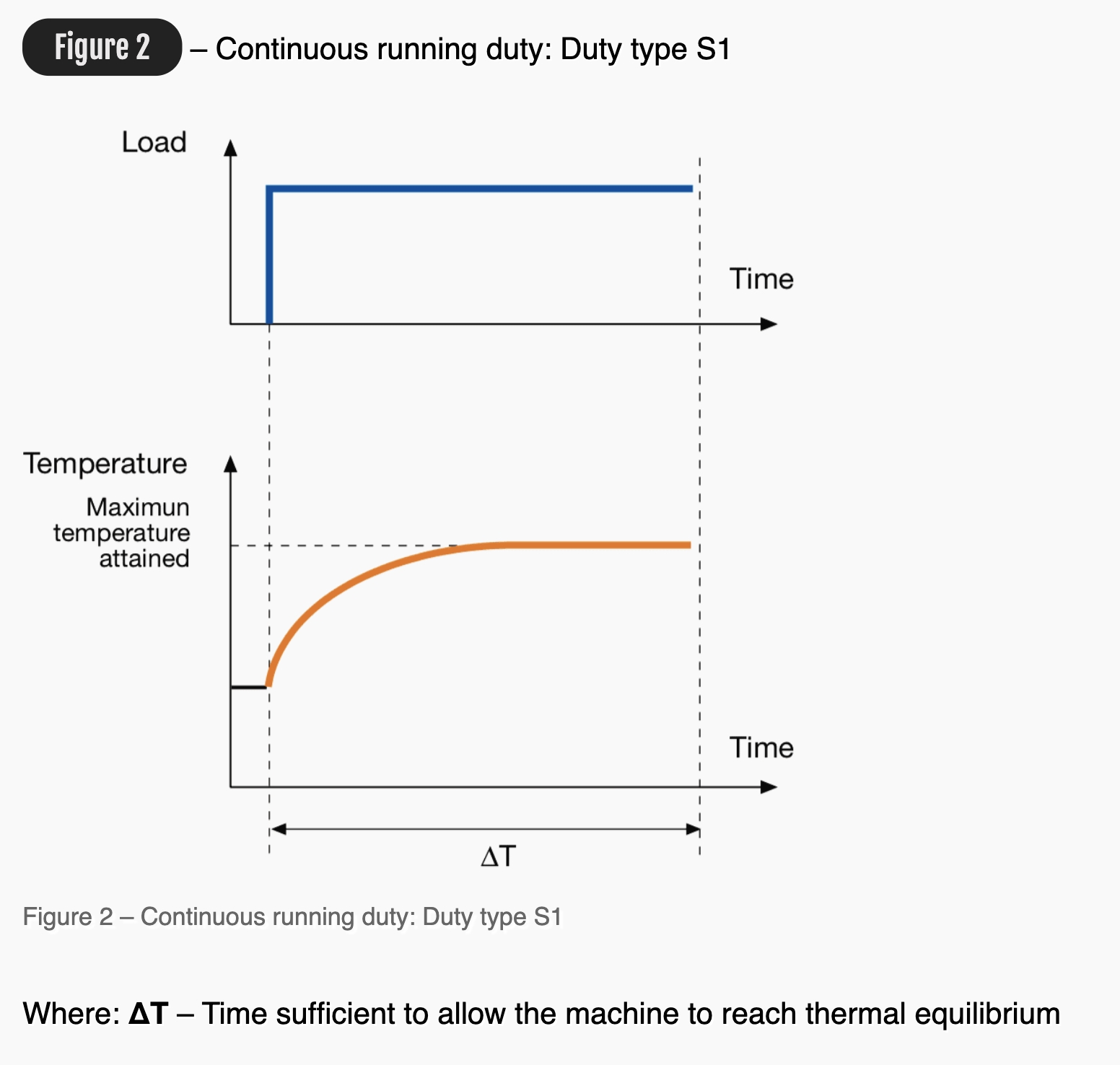
S1 : Continuous running duty
The duty type S1 can be defined as operation at a constant load maintained for sufficient time to allow the machine to reach thermal equilibrium.
For a motor suitable to this duty type, the rating at which the machine may be operated for an unlimited period is specified.
This class of rating corresponds to the duty type whose appropriate abbreviation is S1.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
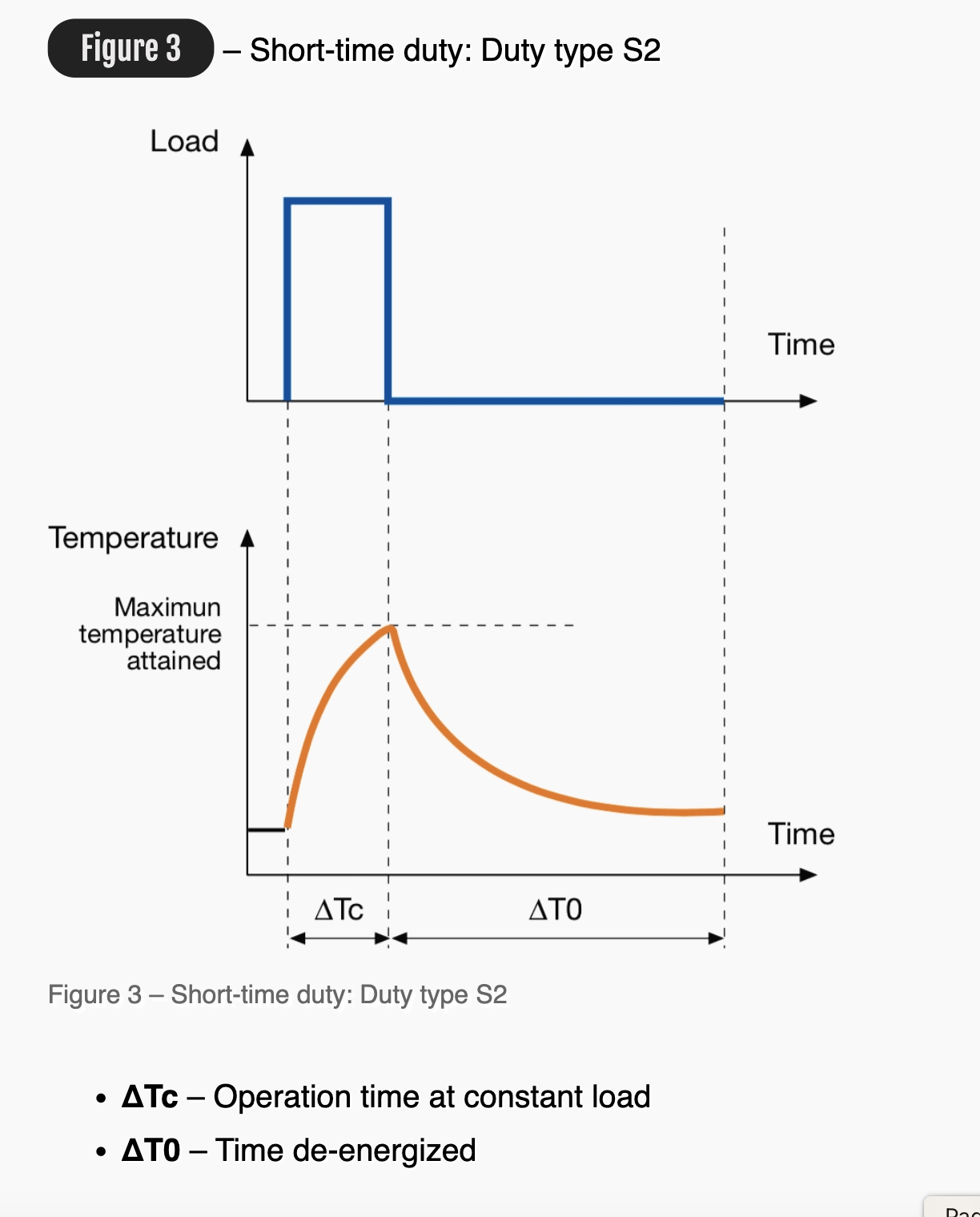
S2 : Short time duty
The duty type S2 can be defined as operation at constant load for a given time, less than that required to reach thermal equilibrium, followed by a time de-energized and at rest of sufficient duration to re-establish the equilibrium between the machine temperature and that of the coolant temperature.
For a motor suitable to this duty type, the rating at which the machine, starting at ambient temperature, may be operated for a limited period is specified. This class of rating corresponds to the duty type whose appropriate abbreviation is S2
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
S3 : Intermittent periodic duty
The duty type S3 is defined as a sequence of identical duty cycles, each including a time of operation at constant load and a time de-energized and at rest. The contribution to the temperaturerise given by the starting phase is negligible
A complete designation provides the abbreviation of the duty type followed by the indication of the cyclic duration factor (S3 30%).
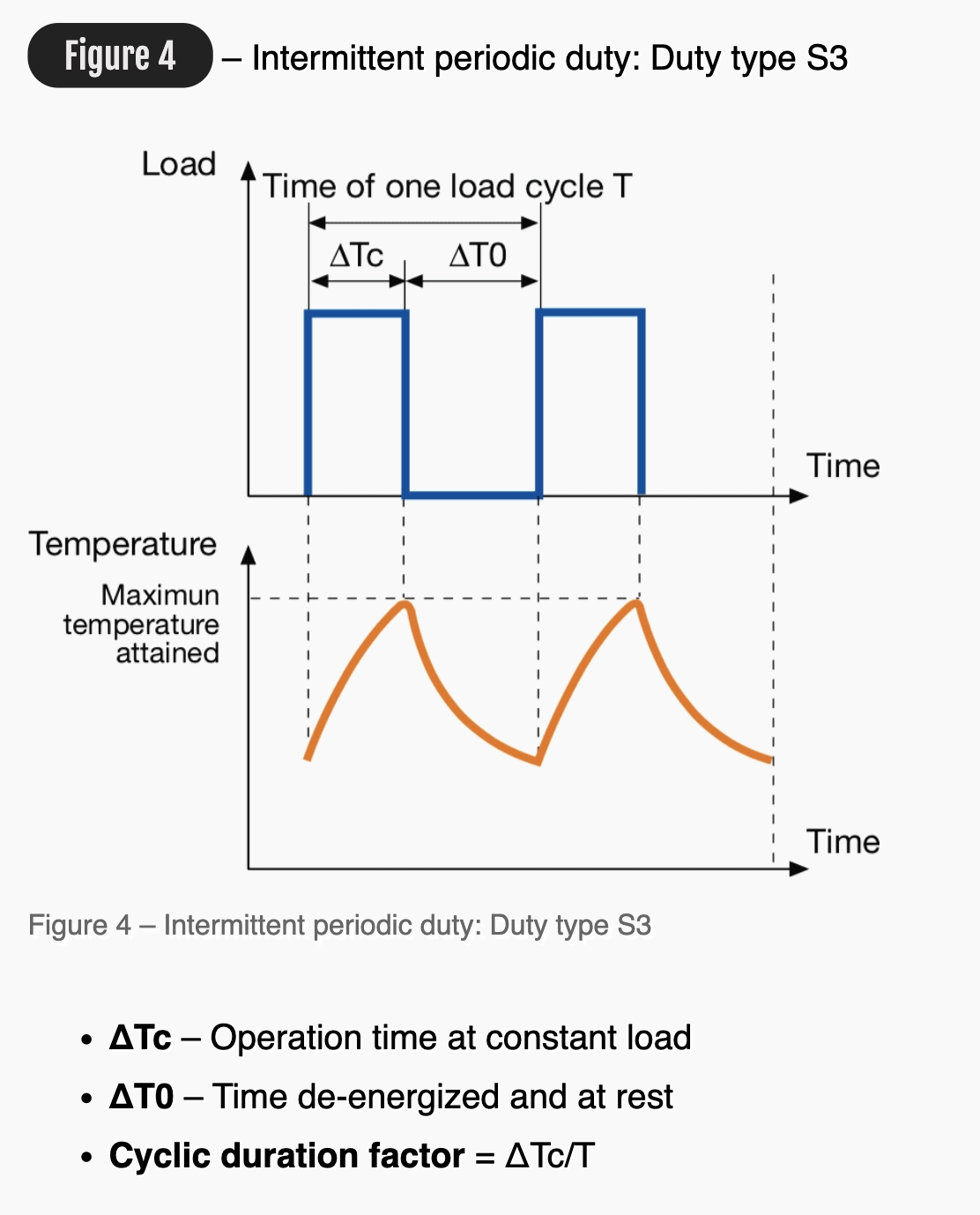
Figure 4 : Intermittent periodic duty: Duty type S3
ΔTc Operation time at constant load
ΔT0 Time de-energized and at rest
Cyclic duration factor = ΔTc/T
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
S4 : Intermittent periodic duty with starting
The duty type S4 is defined as a sequence of identical duty cycles, each cycle including a significant starting time, a time of operation at constant load and a time de-energized and at a rest.
A complete designation provides the abbreviation of the duty type followed by the indication of the cyclic duration factor, by the moment of inertia of the motor JM and by the moment of inertia of the load JL, both referred to the motor shaft (S4 20% JM = 0.15 kg m2 JL = 0.7 kg m2)
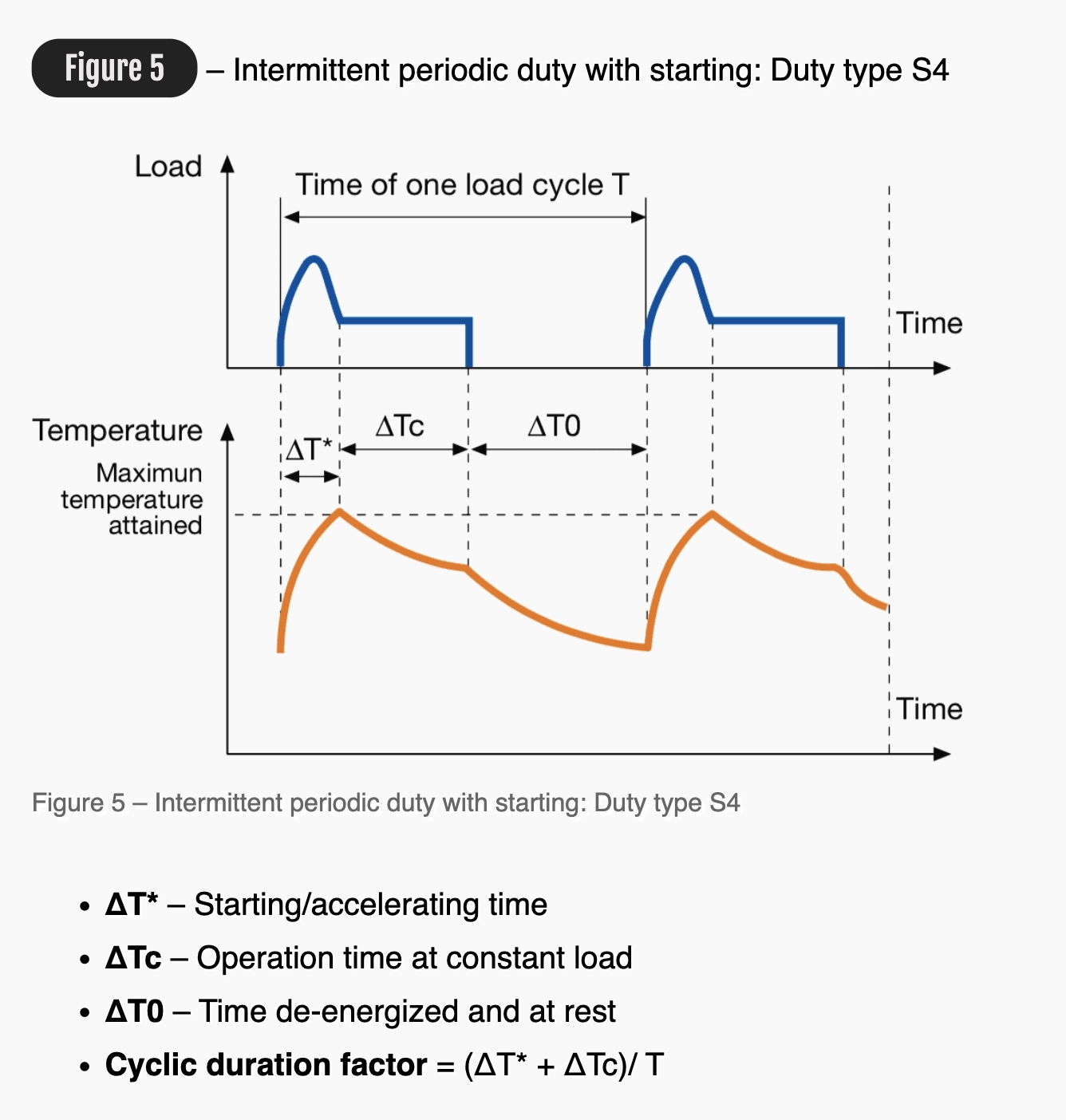
Figure 5 Intermittent periodic duty with starting: Duty type S4
ΔT* Starting/accelerating time
ΔTc Operation time at constant load
ΔT0 Time de-energized and at rest
Cyclic duration factor = (ΔT* + ΔTc)/ T
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
S5 : Intermittent periodic duty with electric braking
The duty type S5 is defined as a sequence of identical duty cycles, each cycle consisting of a starting time, a time of operation at constant load, a time of electric braking and a time de-energized and at a rest.
A complete designation refers to the duty type and gives the same type of indication of the previous case.
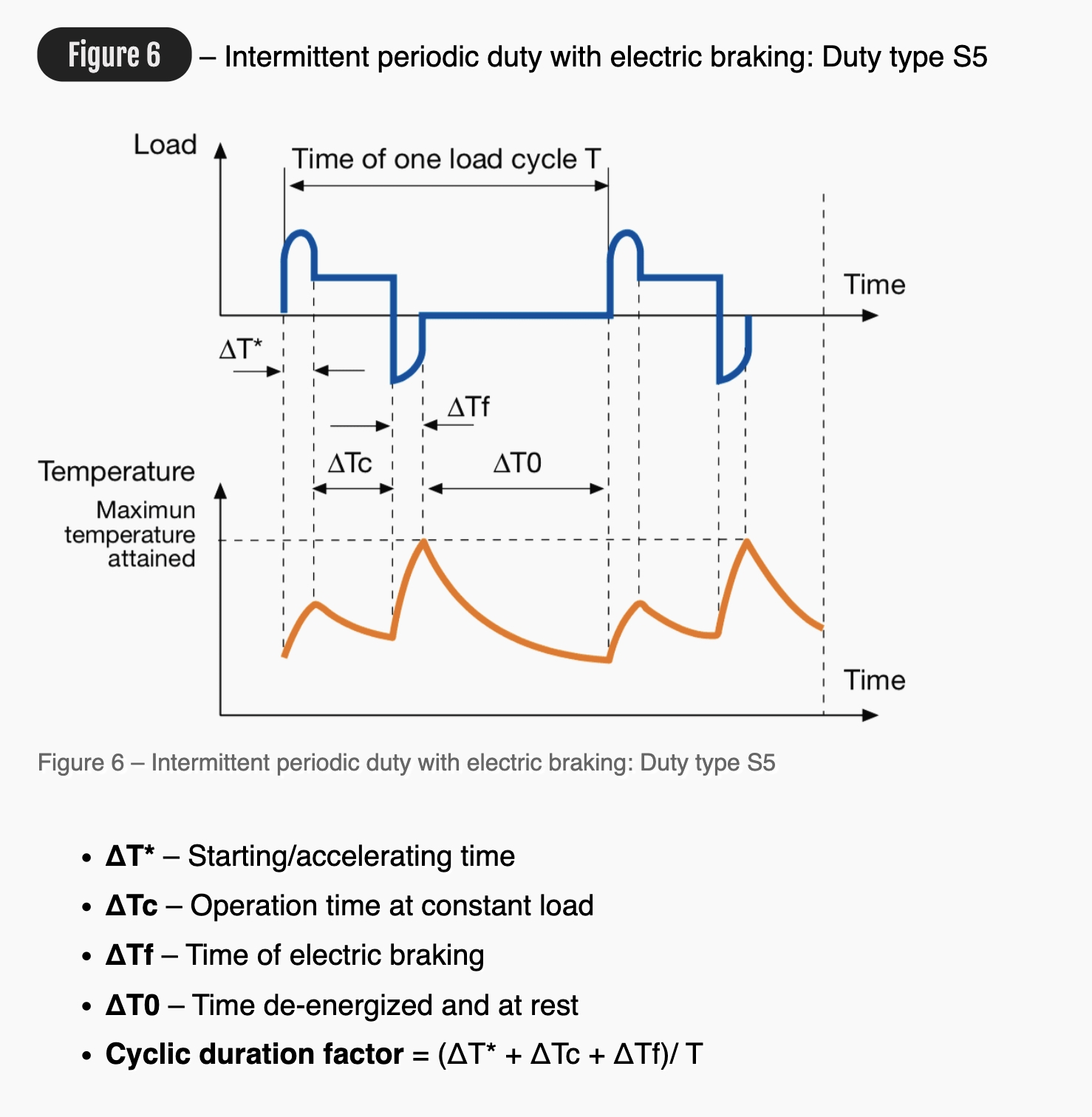
Figure 6 Intermittent periodic duty with electric braking: Duty type S5
ΔT* Starting/accelerating time
ΔTc Operation time at constant load
ΔTf Time of electric braking
ΔT0 Time de-energized and at rest
Cyclic duration factor = (ΔT* + ΔTc + ΔTf)/ T
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
S6 : Continuous operation periodic duty
The duty type S6 is defined as a sequence of identical duty cycles, each cycle consisting of a time of operation at constant load and a time of operation at no-load. There is no time de-energized and at rest.
A complete designation provides the abbreviation of the duty type followed by the indication of the cyclic duration factor (S6 30%).
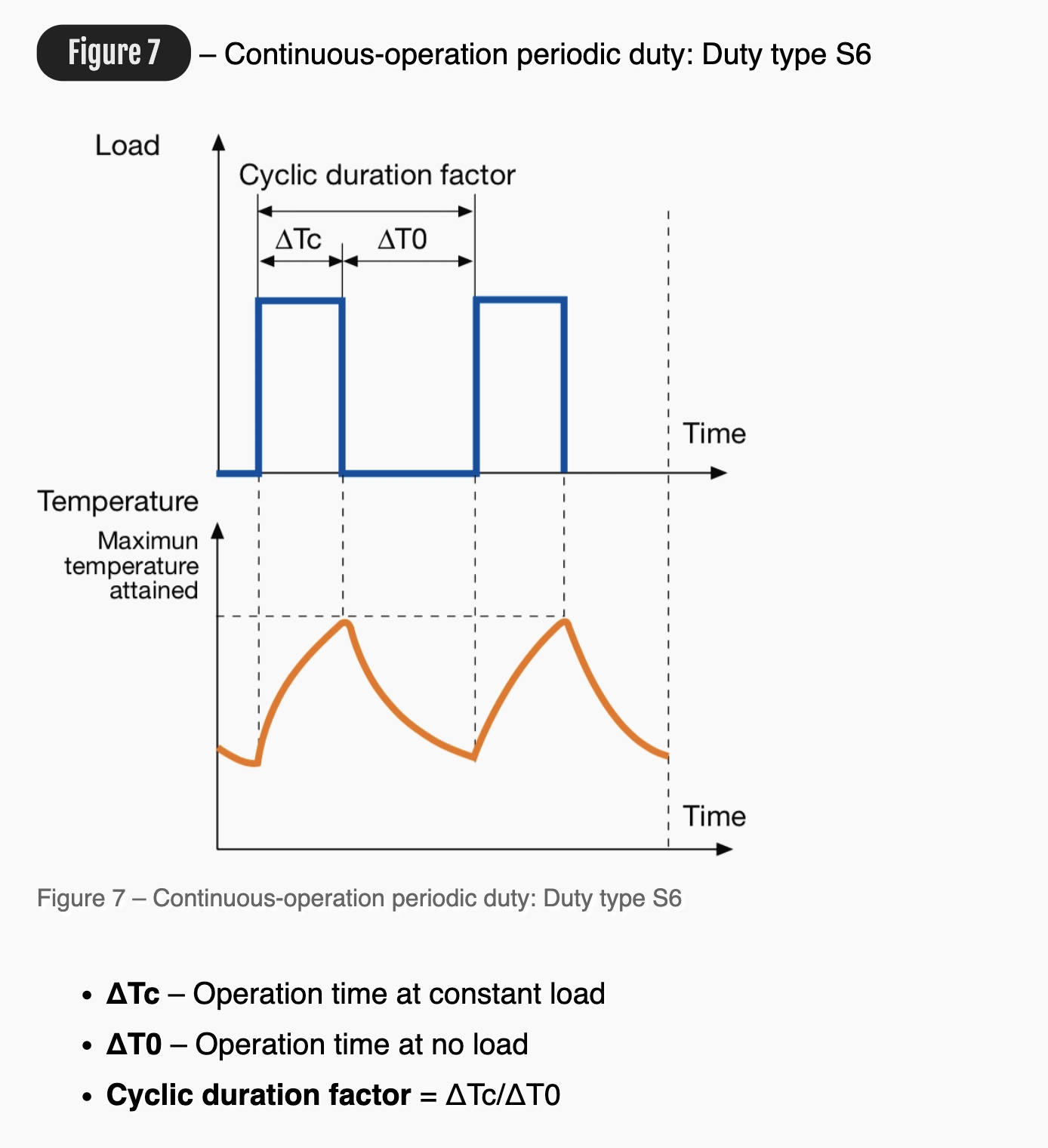
Figure 7 Continuous-operation periodic duty: Duty type S6
ΔT* Operation time at constant load
ΔT0 Operation time at no load
Cyclic duration factor = ΔTc/ΔT0
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________